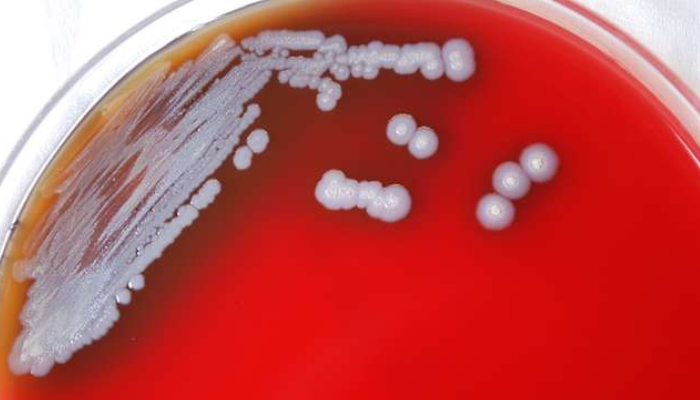
by David Tanedo | Mar 25, 2025 | Bug Library
Burkholderia Pseudomallei What is it? Melioidosis is a disease of humans and animals that is caused by the bacterium Burkholderia pseudomallei, a small gram negative aerobic bacillus. While Burkholderia pseudomallei is found around the world in warm and humid...
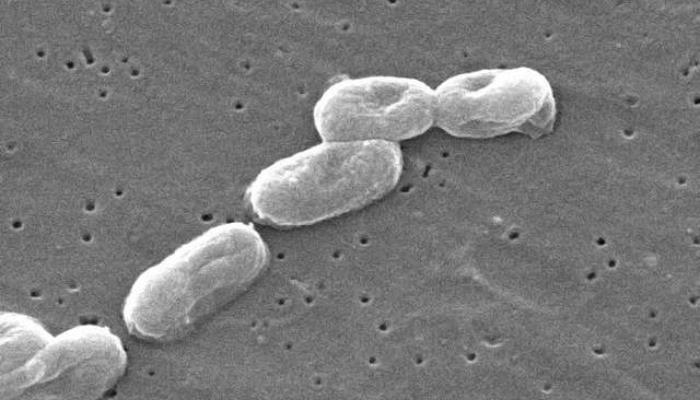
by David Tanedo | Feb 25, 2025 | Bug Library
Burkholderia cepacia (B. cepacia) Burkholderia cepacia (B. cepacia) is a gram-negative, motile, non-spore-forming bacterium. It is a species of bacteria within the Burkholderia cepacia complex (Bcc), a group of closely related bacteria that are often associated with...
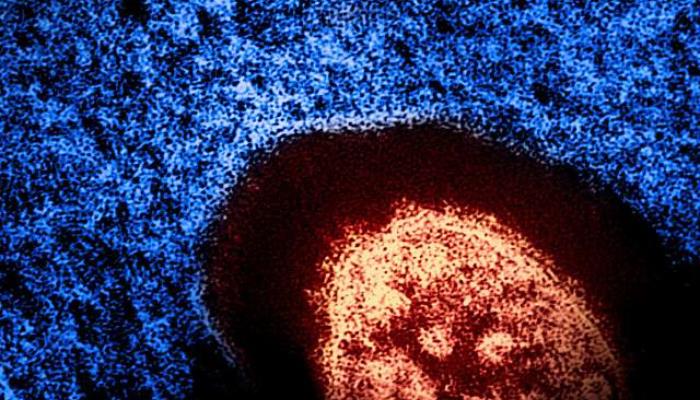
by David Tanedo | Jan 25, 2025 | Bug Library
What is it? Measles is a highly infectious acute viral disease, that can cause serious medical complications. In 2014 the World Health Organization (WHO) declared Australia to have eliminated endemic measles through an effective vaccination program, with most cases...
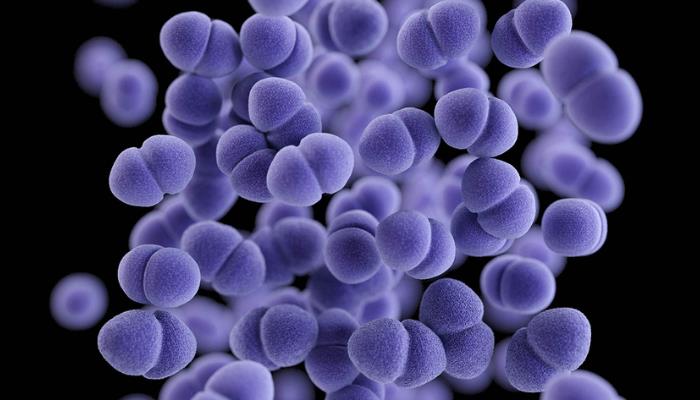
by David Tanedo | Dec 25, 2024 | Bug Library
Linezolid-resistant enterococci (LRE) and linezolid-resistant vancomycin-resistant enterococci (LR-VRE) Linezolid-resistant enterococci (LRE) and linezolid-resistant vancomycin-resistant enterococci (LR-VRE) are emerging as significant concerns in healthcare...
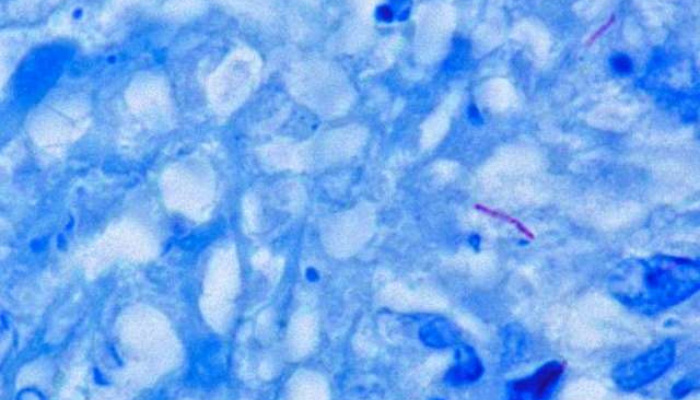
by David Tanedo | Nov 27, 2024 | Bug Library
Mycobacterium tuberculosis What is it? Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis) is the bacterium that causes Tuberculosis (TB) an infectious disease that damages the lungs and other parts of the body. There are 2 types of TB, latent TB infection when someone is...
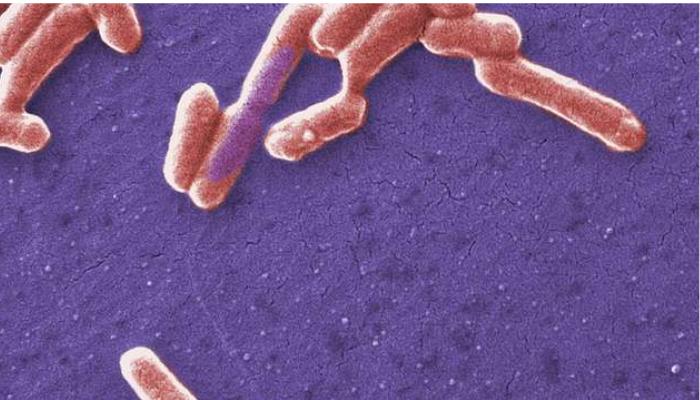
by David Tanedo | Oct 25, 2024 | Bug Library
Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) is a gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium commonly found in the intestines of humans and animals. It was first identified by Theodor Escherich in 1885. While most strains are harmless or even beneficial, some can...








